As more OEM’s focus on product innovation surrounding ergonomics and aesthetics, we have seen increased demand for TPE usage in plastic parts and assemblies. So, what is a TPE? The answer can be complex depending on the intended use, environment, and performance expectations.
TPEs are soft and flexible like elastomers/rubber but can be processed with conventional fabrication techniques (injection molding, extrusion, etc.) and reprocessed like a thermoplastic. Simply put, there are many types of elastomers that fall under the TPE umbrella, and choosing the right one for an application can be a tricky process. Temperature and chemical resistance, overmold bonding, hardness, and tactile feel are just some of the qualifying factors to review when selecting the best TPE for a new or existing application.
Almost all TPEs contain two or more distinct polymeric phases: hard and soft. Their properties depend on the chemistry phases being finely and intimately mixed. Below are some common examples of TPE chemistries:
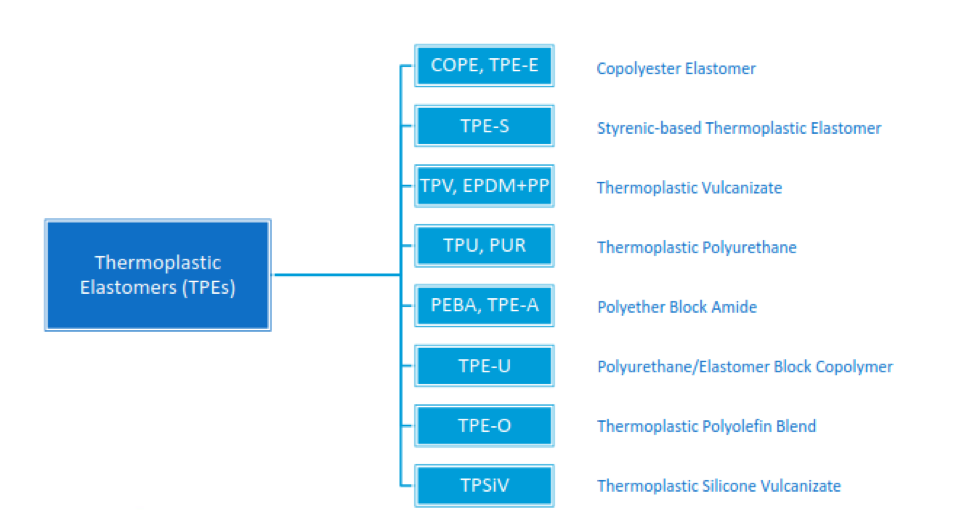
Chase Plastics offers one of the largest thermoplastic elastomer offerings in plastics distribution. Please see the attached guide for a deeper look at our extensive soft product portfolio. Our team is here to provide insight into the many types of TPE’s available in the market. Whether you are looking for a particular part performance, or a basic education, our sales and engineering teams are ready to answer any questions you may have. Contact us today to see how our technical expertise, diverse product line, and outrageous customer service can help take your product from resin to reality!

